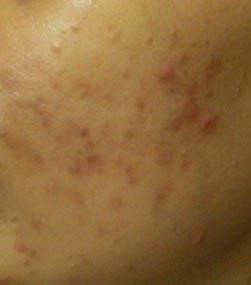
Acne is a chronic inflammatory disease of the pilo sebaceous follicles characterized by comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), papules, pustules, nodules and often scars.
Who gets acne?
Close to 100% of people between the ages of twelve and seventeen have at least an occasional whitehead, blackhead or pimple regardless of race or ethnicity. Acne starts between the ages of ten and thirteen and usually lasts for five to ten years; however, acne can persist into the late twenties or thirties or even beyond. Some people get acne for the first time as adults and this is known as adult acne.
What are the causes of acne?
Bacteria Bacteria that normally live on the skin play a role in acne development. The bacteria are known as Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes). The bacteria content can increase in people whose faces are not clean.
Hormones
During the teen years increased levels of sex hormones cause the oil glands of the skin to produce increased amount of oil. These excess skin oils tend to bind with cellular debris causing a blockage and producing a fertile environment for the bacteria to grow. The bacteria cause inflammation, pus, swelling and redness.
In adult acne, excessive hormones produced due to polycystic ovaries and other hormonal imbalances cause excess oil production and inflammation, which lead to acne.
What are the factors that precipitate or aggravate acne?
Stress - Stress is frequently implicated in aggravation of acne while acne itself induces stress.
Sweat - sweating in a hot and humid environment causes deterioration in 15% of acne patients.
Menstruation - Pre menstrual flare of acne occurs in 70% of female acne patients.
Friction and pressure - Friction and pressure from helmets, backpacks and tight collars can induce blackheads and papules. Pressure from face massages or facials can aggravate acne.
Pregnancy - Pregnancy has an unpredictable effect on acne. Pre-existing acne may aggravate or remit during pregnancy.
Diet - High glycemic load foods (sugar loaded and starchy foods), oily foods may aggravate acne.
Drugs - Oral contraceptives, anti tuberculosis medication, oral steroids, anti depressants may aggravate acne.
Treatment modalities in Acne
Topical therapy (medicated creams)
Benzoyl Peroxide
This is a common topical treatment. It has 3 actions – it kills bacteria, reduces inflammations and helps to unplug blocked pores. It comes in different brand names and varying strengths i.e., 2.5 %, 4%, 5% and 10%.
Topical Antibiotics
There are various antibiotics preparations such as Clindamycin, Clarithromycin, Erythromycin and Nadifloxacin. They reduce the number of bacteria and reduce inflammation and are to be used for at least 8 weeks.
Retinoids
These are good at unplugging blocked pores. They include Adapalene, Tretinoin and Isotretinoin. When you use a tropical retinoid, you may develop some skin redness and skin peeling. Therefore it may require to be used with a moisturizer and it is best to apply this preparation after sunset or at night. The most common side effects are burning, irritation and dryness. Therefore you may be advised to first use a low strength, less frequent application and for a shorter duration and gradually increase the time of contact.
Azelaic acid
It has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. It also helps to decrease hyper pigmentation caused by acne. It is available as 10% and 20 % cream. Using it in combination with other topical medications may increase the efficacy of Azelaic acid.
Oral Medication
Antibiotics
These include Minocycline, Doxycycline, Azithromycin and Erythromycin. Antibiotics target bacteria and inflammation. They are administered for approximately 4-8 weeks till inflammatory lesions cease to erupt and in some cases for a longer time. Courses maybe repeated if necessary.
Isotretinoin
This is a synthetic derivative of Vitamin A. It reduces the sebum production from the sebaceous glands (oil glands). It normalizes ductal hypercornification and prevents clogging of pores. It is the most comedolytic of all anti acne agents. It indirectly lowers the bacterial count on the skin and exerts an anti-inflammatory effect. It is effective in boys and girls of all age groups. It is useful in severe nodulocystic acne, fulminant acne, difficult/recalcitrant acne and moderate acne if scarring is imminent. Women should avoid taking the drug for 3-6 months before planning a family. The drug can be given daily for 5-6 months or as a pulse dose i.e. for 7 to 10 days per month for a longer period of time. It can be combined with oral antibiotics or hormonal treatment depending on the case. A blood test is required before starting the medication and at 4 and 8 weeks thereafter. Skin care advice of using a sunscreen, moisturizing cream and lip moisturizers should be followed while on the drug.
Hormonal Treatment.
Hormonal therapy is an excellent choice for female patients with acne who may have one or more of the following:
- Acne- persistent or late onset, lower face involvement, pre menstrual flare-up
- Hirsuitism- Characterized by thick dark facial hair.
- Androgenetic Alopecia- Frontal scalp hair thinning
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome- diagnosed on hormonal evaluation or ultrasonography of the pelvis.
- Other hormonal imbalances - due to adrenal glad or pituitary gland over activity.
Specific hormonal therapies may be divided into two groups. One group blocks androgen receptors and is known as anti androgens. It includes medication like Cypreterone Acetate, Spironolactone, Drospirenone and Finesteride. The other group decreases androgen production by the ovaries and adrenals include oral contraceptives and Glucocorticoids.
A combination of anti androgen and oral contraceptive is available consisting of Cyproterone acetate 2mg with Ethinyl estradiol 35mg in the treatment of acne known as Diane 35. Another consideration is Drospirenone 3.00mg and Ethinyl estradiol 0.030mg known as Yasmin. It is typically given for 6-12 months but may be given for 2 years or longer with appropriate breaks when well tolerated and needed. It can be combined with oral antibiotics, oral Isotretenoin and other adjunctive acne therapy.
Physical modalities in treatment of Acne
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels for acne work by removing the surface layers of the skin in order to expose the fresh and unaffected layers below. Done in a series of four to six sessions, these peels can improve mild to moderately severe cases of acne, and can be given over the face or other body area where acne is a problem. Chemical peels don't really peel the skin, despite what the name implies. They rapidly exfoliate the skin, allowing dead skin cells to shed more effectively. By keeping dead skin cells and excess oil from clogging the hair follicle, pore blockages (comedones) and can drastically reduce breakouts of papules and pustules.
Chemical peels fall into a broad category of Alpha Hydroxy acids (AHAs) or Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs). Glycolic acid is the most commonly used AHA and Salicylic Acid is the most commonly used BHA in the treatment of acne.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is done to reduce the oiliness in acne prone skins. It also helps reduce superficial acne scarring.
Intralesional Corticosteroids
A steroid injection is delivered into larger pimples ie nodules and cysts to reduce inflammation.
Blue Light and Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
These are light and laser systems, which are used, in some medical centers to treat acne.