What is Vitiligo?
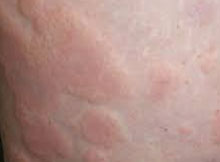
Vitiligo is a skin disorder in which patients develop white spots on the skin that vary in size and location. These spots occur when pigment cells called "melanocytes" are destroyed and the pigment melanin can no longer be produced. Pigment cells are present throughout the skin, hair, mouth, eyes and some part of the nervous system and they can be damaged or destroyed in any of these areas.
Who gets Vitiligo?
Vitiligo affects at least 1% of the population. About 30% of all Vitiligo patients say that other family members also have this condition. Even though most people with Vitiligo are in good general health, they face a greater risk of having hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, vitamin B12 deficiency, Addison's disease (adrenal dysfunction), Alopecia areata (round patches of hair loss) and or uveitis (inflammation with the eyes).
About 50% of all Vitiligo patients develop the disease in childhood/adolescence before the age of 20. Although largely similar to the disease in adults, childhood Vitiligo is a distinct subset of Vitiligo with a higher incidence of family history of autoimmune or endocrine diseases, early or premature graying and poor response o topical PUVA.
What is the cause of Vitiligo?
The precise cause of Vitiligo is not known. A combination of genetic, immunological and neurogenic factors is of major importance in most cases. Trauma of any kind (physical, mechanical, chemical, emotional) too can trigger off the disease process. Stress is often implicated as a trigger factor.
What is the treatment for Vitiligo?
Treatment is to try restore the pigment i.e repigmentation in the patches. However, one cannot predict the course and final outcome of this condition.
What is the treatment for Vitiligo?
a) Photo-chemotherapeutic treatment (PUVA Therapy): In this photosensisting agents are taken either orally or topically followed by exposure to ultraviolet A (UVA) light. Commonly used psoralens are (8-methoxy psoralens or 4,5,8trimethyl psoralens).
b) Corticosteroids: These are used topically or orally depending upon the severity of the disease. They are often used as an attempt to check the spread of the disease.
c) Immunomodulators: These drugs can be used in the maintenance phase of the disease. Commonly used immunomodulators are Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus. They help in bringing back the colour and also help to control the spread of the disease. They can be safely applied over a long period of time. Levamisole is a non-specific immuno modulatory oral drug, which may help in controlling the spread of Vitiligo in some cases. It can be used in children too.
d) Pseudocatalase: It is a newer modality of treatment. It is applied locally on the Vitiligo patch and is giving promising results.
e) Narrow band UVB Phototheraphy: Narrow Band UVB for the treatment of Vitiligo has recently emerged as a promising therapy. It is the safest and most effective therapy for generalized Vitiligo. With best results on the face and neck and in Vitiligo present for shorter duration.
It involves the delivery of specific wavelength of UVB-311mm in a UVB chamber. Both adults and children can be treated with it. It has to be given 2-3 times per week. A minimum number of 15 to 20 sessions are required for optimal results.
f) Targeted NB UVB Phototherapy: It is a variation of NB-UVB. In targeted phototherapy, the beam is focused only on areas affected by Vitiligo. It is a treatment of choice in patients with less than 30% body surface area involvement and the best treatment for children as the cumulative doze of radiation is very low and avoids needless exposure of uninvolved skin.
g) Monochromatic Excimer Laser: The xenon chloride gas ecximer laser offers a mean of delivering local monochromatic 308nm UV Phototherapy to the skin without photo thermal effects. Because the laser energy is delivered through a flexible hand piece, the adjacent normal skin is left untouched.
h) Excilite: It is a monochromatic examer light source (MEL @ 308nm) for fast treatment of Vitiligo. It is designed for the treatment of therapy resistant Vitiligo lesions on the skin and enables targeted exposure. It requires less time than other UV therapies including ecximer laser as it allows larger areas to be treated.
i) UVA/UVB Phototherapy: This allows delivery of light in the waveband of UVB and UVA 1(300-380nm) both to target and treat stubborn Vitiligo patches.
j) Depigmenting agents: This treatment is reserved for patients in whom Vitiligo has affected 90% of the body and only a few dark patches of normal skin or areas of pigment remain. In such cases topical monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone is used to remove the colour from the remaining pigmented areas in order to achieve a more uniform colour.
Radio surgery: In this procedure, radio waves are used in ablative mode, to ablate the unwanted layers of the skin and flatten out the edges of scars and to promote collagen remodeling thereby filling up deep irregular scars.
Steroid injections - Intralesional Steroid Injections like Triamcinolone Acetonide 10mg-40mg may be used for raised keloidal and hypertrophic scars. These injections help to soften thick stubborn fibrous tissue.
Subcision – This involves subcutaneous sectioning of dermal adhesions with a sharp needle thereby lifting the scars. This technique is useful for very deep-pitted scars. ice pick scars, boxcar scars and rolled scars.
Surgical treatment
Different techniques such as surgical excision, dermabrassion, tattooing, punch grafting, split skin Grafting and transplantation of invitro cultured epidermis-bearing melanocytes, it is reserved for stable cases with few localized stubborn patches.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Vitiligo contagious?
No, Vitiligo does not spread from one person to the other.
Does diet have any role in Vitiligo?
There are no particular dietary items that are known to cause or triggers Vitiligo.
Vitiligo and Leucoderma the same thing?
Vitiligo is the dermatological term used. Leucoderma translates as white patches and could be due to reasons other than Vitiligo. Vitiligo is the dermatological term for white patches for autoimmune origin.
Does stress worsen or trigger Vitiligo?
Stress has been scientifically proven through various studies as a trigger.
Is there any way of preventing new lesions?
Patients should always protect their skin against excessive sun exposure. Vitiligo patients must avoid wearing artificial jewellery containing nickel, cobalt and other metals. Plastic slippers, bindies, hair dyes, fragrance can induce chemical Leucoderma. Patients should protect themselves against injury and friction on the skin.
Is there a cure for Vitiligo?
Usually with continuous treatment and by doing a combination of treatments, a number of cases improve or clear. This may take a year or more. However there are certain stubborn areas like the tips of fingers and toes, lips, bony prominences that may take longer or not respond at all to treatment.
What is the future of Vitiligo?
There is a lot of research going on regarding Vitiligo. "Stem Cell" therapy may change the way Vitiligo is treated. The future holds some promise.